8 - @OneToOne & @OneToMany : ASSOCIATION UNIRECTIONNELLE DE 1 VERS n (client04)
TRAVAIL A REALISER :
-
mettre en place une association unidirectionnelle de un vers plusieurs entre Client et Telephone.
- créer le projet client04
- recopier le contenu du projet client03
- ajouter la classe Telephone
- modifier la classe Client
La classe entité Telephone comportera les attributs suivants :
private int id;
private String numero;
private int type;
- La clé primaire id sera autogénérée.
La classe Client comportera un attribut supplémentaire telephones :
Un Client peut avoir plusieurs Téléphones. L’attribut telephones est une Collection d’objets de type Téléphone.
Un petit coup de pouce :
private int id;
private String nom;
private String prenom;
private Adresse adresse;
private Collection<Telephone> telephones;
Mise en place de l’association unidirectionnelle de 1 vers n
La navigabilité de l’association est de Client vers Telephone.
L’annotation @OneToMany sur la méthode getTelephones() de Client indique la navigabilité de Client vers Telephone.
@OneToMany(cascade={CascadeType.ALL}, fetch=FetchType.EAGER)
public Collection<Telephone> getTelephones() {
return telephones;
}
L’absence d’attribut client dans la classe Telephone indique le caractère unidirectionnel de l’association. Cela signifie que depuis un objet Téléphone, on ne peut pas accèder au Client qui y est associé.
- Créez les repositories nécessaires
Code du Contrôleur :
@CrossOrigin("*")
@RestController
public class ClientController {
@Autowired
private ClientRepository clientRepository;
@Autowired
private AdresseRepository adresseRepository;
@Autowired
private TelephoneRepository telephoneRepository;
@GetMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
public String home()
{
Adresse adresse1=new Adresse("5, rue du Renard","","75015","PARIS", "FRANCE");
Client client1=new Client("MARTIN","Jean");
client1=clientRepository.saveAndFlush(client1);
Adresse adresse2=new Adresse("5, rue du Renard","","75015","PARIS","FRANCE");
Client client2=new Client("DUPONT","sophie",adresse2);
adresse2.setClient(client2);
client2=clientRepository.saveAndFlush(client2);
Adresse adresse3=new Adresse("20, boulevard Gambetta","","78300","POISSY","FRANCE");
Client client3=new Client("DURAND","Pierre",adresse3);
adresse3.setClient(client3);
client3=clientRepository.saveAndFlush(client3);
Adresse adresse4=new Adresse("29, boulevard Devaux","","78300","POISSY","FRANCE");
Client client4=new Client("MADEC","Denis",adresse4);
adresse4.setClient(client4);
client4=clientRepository.saveAndFlush(client4);
System.out.println("liste de tous les clients:");
Collection<Client> liste=clientRepository.findAll();
affiche(liste);
System.out.println("MARTIN Jean habite desormais avec DUPONT Sophie");
client1.setAdresse(adresse1);
adresse1.setClient(client1);
clientRepository.save(client1);
// System.out.println("MADEC Denis se desinscrit");
// clientRepository.delete(client4);
System.out.println("Liste de toutes les adresses et les clients associés:");
Collection<Adresse> listeAdresses = adresseRepository.findAll();
for (Adresse adresse : listeAdresses)
{
System.out.print(adresse+" client : ");
if (adresse.getClient()!=null) System.out.println(adresse.getClient());
}
Telephone tel1=new Telephone("01 43 65 87 34");
telephoneRepository.save(tel1);
System.out.println("le numero "+tel1.getNumero()+" est ajoute au client "+client1);
ajoutTelephone(client1.getId(),tel1);
Telephone tel2=new Telephone("01 65 34 01 23");
telephoneRepository.save(tel2);
System.out.println("le numero "+tel2.getNumero()+" est ajoute au client "+client2);
ajoutTelephone(client2.getId(),tel2);
Telephone tel3=new Telephone("02 78 99 41 73");
telephoneRepository.save(tel3);
System.out.println("le numero "+tel3.getNumero()+" est ajoute au client "+client3);
ajoutTelephone(client3.getId(),tel3);
Telephone tel4=new Telephone("02 65 98 23 08");
telephoneRepository.save(tel4);
System.out.println("le numero "+tel4.getNumero()+" est ajoute au client "+client3);
ajoutTelephone(client3.getId(),tel4);
System.out.println("liste de tous les clients:");
liste=clientRepository.findAll();
affiche(liste);
System.out.println("le numero "+tel2.getNumero()+" est supprime du client "+client2);
enleveTelephone(client2.getId(),tel2);
System.out.println("Liste de tous les clients:");
this.affiche(clientRepository.findAll());
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("<h1>Regardez dans votre console et dans votre base de données MySQL <strong>JPA</strong></h1>");
sb.append("<a href='http://localhost:8080/clients'>Voir la liste des clients enregistrés</a>");
return sb.toString();
}
@GetMapping(value = "/clients")
public ResponseEntity<?> getAll(){
List<Client> liste = null;
try
{
liste = clientRepository.findAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND).body(null);
}
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(liste);
}
/**
* Méthode pour affichage dans la console
* @param liste
*/
private void affiche(Collection<Client> liste)
{
for (Client client : liste) {
System.out.println(client);
}
}
private boolean ajoutTelephone(int idClient,Telephone numero){
// on recherche le client
Client cl=clientRepository.getOne(idClient);
if(cl!=null)
{
// on ajoute le numéro de téléphone
cl.getTelephones().add(numero);
clientRepository.saveAndFlush(cl);
return true;
}
return false;
}
private boolean enleveTelephone(int idClient,Telephone numero){
Client cl=clientRepository.getOne(idClient);
if(cl!=null)
{
for(Telephone num : cl.getTelephones())
{
if(num.equals(numero))
{
cl.getTelephones().remove(num);
telephoneRepository.delete(num);
clientRepository.saveAndFlush(cl);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
- lancer l’application, allez votre sur votre navigateur à l’adresse habituelle et observer la BD
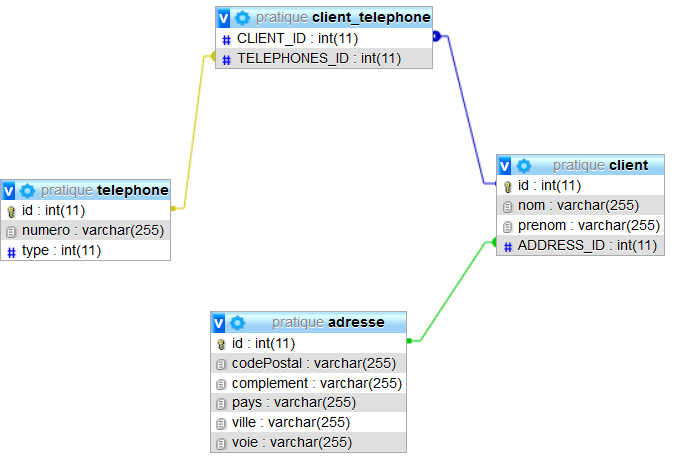
Voici ce que vous devez obtenir comme base de données sous MySQL :
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `adresse` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`codePostal` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`complement` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`pays` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`ville` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`voie` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `client` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`nom` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`prenom` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`ADDRESS_ID` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `ADDRESS_ID` (`ADDRESS_ID`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `client_telephone` (
`CLIENT_ID` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`TELEPHONES_ID` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
KEY `CLIENT_ID` (`CLIENT_ID`),
KEY `TELEPHONES_ID` (`TELEPHONES_ID`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `telephone` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`numero` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`type` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
--
-- Contraintes pour la table `client`
--
ALTER TABLE `client`
ADD CONSTRAINT `client_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`ADDRESS_ID`) REFERENCES `adresse` (`id`);
--
-- Contraintes pour la table `client_telephone`
--
ALTER TABLE `client_telephone`
ADD CONSTRAINT `client_telephone_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`CLIENT_ID`) REFERENCES `client` (`id`),
ADD CONSTRAINT `client_telephone_ibfk_2` FOREIGN KEY (`TELEPHONES_ID`) REFERENCES `telephone` (`id`);